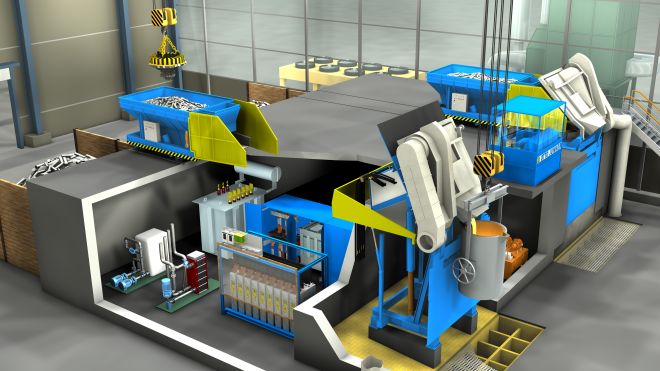
The foundational advantage of induction melting technology lies in its capability to efficiently and CO2-neutrally melt metals with minimal melting times and precisely controllable movement of the liquid melt.
The key benefit of induction melting technology is that the raw material is heated directly and metallurgically neutrally, avoiding any overheating. We manufacture induction furnaces for the melting, holding, and casting of metals based on both crucible and channel furnace principles. We choose the most suitable technology for each application.
Both types of constructions operate completely CO2-free when powered by electricity from renewable sources.
The induction crucible furnace can operate with either a liquid bath or complete drainage after each batch. An IGBT inverter supplies the furnace with power, and its operating frequency is optimally adapted to the melting material.
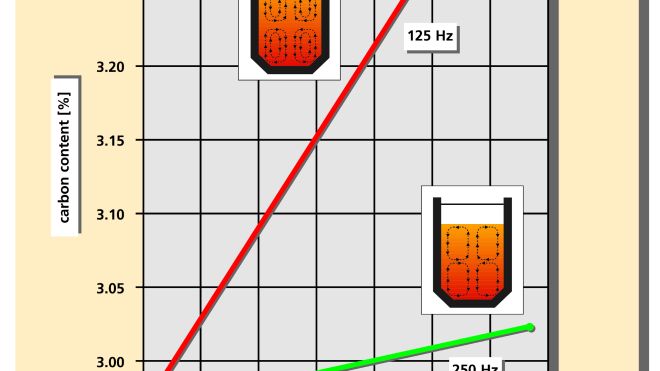
With multi-frequency technology, customers can work with high frequency when starting with small-piece melt material, resulting in a smooth, oxide-free bath surface. For carburizing, alloying, or stirring in chips, the frequency is then switched to a low level, generating high turbulence in the melt bath.
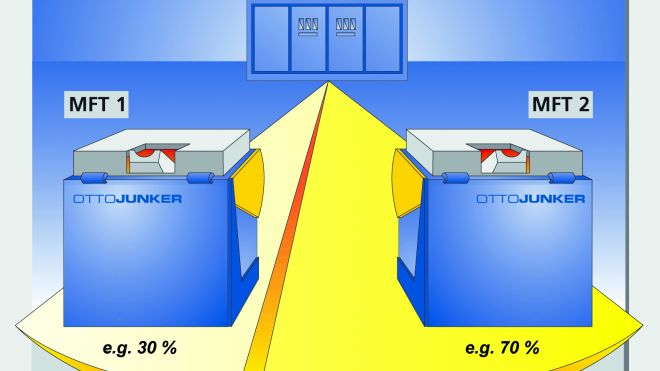
Induction furnace systems are often configured as dual systems: a shared IGBT frequency inverter system feeds two crucible furnaces. This optimally utilizes the installed electrical power: while one furnace is melting, the second can keep the melt warm.
In addition to standardized series, such as the JupiterLine with a capacity of 2 to 8 tons concerning iron, we also offer furnaces designed for the individual use case. The induction crucible furnace can be configured, for example, as a vacuum or protective gas furnace. It is also possible to induce a targeted circulation of the liquid melt through a phased arrangement of partial coils, which is necessary, for instance, in the production of grain refinement alloys.
Benefits at a glance:
- Maximum flexibility through batch operation
- Highest operational reliability through IGBT technology, OCP+ coil monitoring, and StableCoil
- CO2 neutral melting process
- High melting capacities with minimal space requirements
- Enhanced casting quality through precise temperature and analysis control
- Optimal start-up conditions and controlled manipulation of bath movement for alloying and chip melting through multifrequency technology

In the crucible furnace, an alternating current flows through a mostly cylindrical copper coil, generating an electromagnetic field that induces eddy currents in the molten material. The ohmic losses of these currents heat the molten material. Due to the short response time of the coil, temperature control can be quickly and precisely regulated.
After melting, a movement of the molten bath occurs, the intensity of which can be influenced by varying the frequency. This allows for precise alloying, and small materials, such as chips, can homogeneously distribute in the melt.
Induction furnaces are characterized by their high power density. With proper sizing, a crucible furnace can liquefy its entire contents within 30 minutes.
The crucible furnace can be completely emptied, making it particularly suitable for flexible alloy changes and discontinuous batch operation.
The induction crucible furnace is powered by an inverter using either thyristor or transistor technology (IGBT). The constant power regulation ZEUS ensures optimal power coupling even at lower packing densities.
Otto Junker offers water cooling systems, including heat recovery, for cooling coils, yokes, frequency inverters, and power cables. Solutions vary depending on the climate at the installation site, including options like evaporative cooling towers, adiabatic air coolers, or glycol-free frost-resistant air coolers.
To minimize smoke emissions during melting, the furnace systems are equipped with hydraulically folding hoods. Smaller systems may use ring channel exhaust systems.
All Otto Junker induction melting furnaces are controlled by a JuMI (Junker Machine Interface) – a safety PLC with a WinCC Touch Screen visualization. Optionally, all collected data from the melting process can be forwarded to a higher-level database. Moreover, there is the possibility to optimize operating procedures and batch compositions for minimal energy consumption.
High efficiency, low energy consumption
By using highly conductive copper, optimal coil geometry, and IGBT inverter technology, our induction furnaces achieve high energy efficiency. Additionally, for copper and aluminum alloys, a multi-layer energy-saving coil results in additional savings between 7 and 9 percent.
Maximum efficiency
The IGBT technology, combined with parallel resonant circuit technology, enables the realization of an ideal inverter with minimal current load, solely through compensated current, and a constant power factor (cos phi = 0.99 at the inverter input). The furnace coil is secured by strips and remains form-stable even under high current load. Optionally, the coil can be continuously monitored using the laser-optical temperature monitoring system OCP+. The furnace yokes ensure maximum efficiency and minimal operator exposure to stray fields through targeted, low-loss return of the electromagnetic field.
Optimal alloying, carburizing, and chip melting
The Junker parallel resonant circuit inverter makes it possible to operate the furnace system at multiple switchable frequencies. This allows the customer to work with high frequency for the initial melting of small pieces, ensuring a calm, oxide-free bath surface. For carburizing, alloying, or stirring in chips, the frequency can then be switched to a lower setting, generating high turbulence in the melt bath.
Digitalization with the Junker Melting Interface
The Junker Melting Interface – JuMI – optimizes process control and reliably monitors the entire melting operation. The system is based on a safety PLC with a touchscreen WinCC visualization. It provides the user with online support and the ability to connect data to higher-level systems, such as through an OPC UA interface."
| typical application | melting metals |
| design | crucible furnace |
| furnace type | hydraulically tiltable |
| capacity | 0.1 - 100 t (related to iron) |
| model series Jupiter Box Line | 0.1 - 1.5 t |
| model series Jupiter Line | 2 - 8 t |
| model series MFT | 10 - 30 t |
| MFT custom made | 35 - 100 t |
| electrical power | 100 kW - 30,000 kW |
| metal extraction | batch process |
| melting materials | Iron, steel, copper alloys, aluminum, zinc, magnesium, gold, silver, nickel, cobalt, silicon |
Downloads
JUPITER Line EN
pdf | 3,94 MBJUPITER Line DE
pdf | 3,80 MBOCP Plus Englisch
pdf | 6,85 MBOCP Plus Video Deutsch
mp4 | 68,34 MBOCP Plus Video Englisch
mp4 | 68,35 MBOCP Plus Deutsch
pdf | 7,00 MBMedium-Frequency Coreless Induction Furnaces
pdf | 3,19 MBMittelfrequenz-Induktionstiegelöfen
pdf | 3,18 MBOJG-Induktionsofenanlagen-Aluminium-10-2024-DE
pdf | 2,35 MBOJG-Induktionsofenanlagen-Aluminium-10-2024-EN
pdf | 2,34 MB

Phone +49 2473 601-0
+49 2473 601-0

E-Mail sales@otto-junker.com
sales@otto-junker.com